Your AI Isn’t Slow. Your Data Is.
Table of Contents
AI system feels slow or unreliable
AI adoption is no longer limited to tech giants. Startups, mid-size enterprises, and large organizations are all integrating
Teams often blame the model when their AI system feels slow or unreliable:
“The LLM is taking forever to respond!”
“The results feel inconsistent.”
“Token usage is too high.”
“RAG is not improving accuracy.”
But in 90% of cases, the model is not the bottleneck —
your data pipeline is.
You’re driving a Ferrari on broken roads.
This blog will walk you through exactly how to fix those roads — step-by-step — so your retrieval, generation, and costs finally match the quality of your LLM.

Why Your AI Feels Slow (Even With a Great Model)
Most AI workloads fail because of one or more data-layer issues:
- Scattered or unindexed data sources
- Slow vector retrieval or poorly configured databases
- Giant documents chunked incorrectly
- Missing metadata or embeddings
- Poor chunking strategy
- No caching or no deduplication
- Retrieval returning irrelevant or redundant data
To understand how embeddings work at a foundational level, it helps to refer to the
OpenAI Embeddings Documentation:
https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings
LLMs are fast.
Bad retrieval is slow.
The diagram below shows the full end-to-end flow of a modern, optimized AI pipeline before we dive into detailed steps:
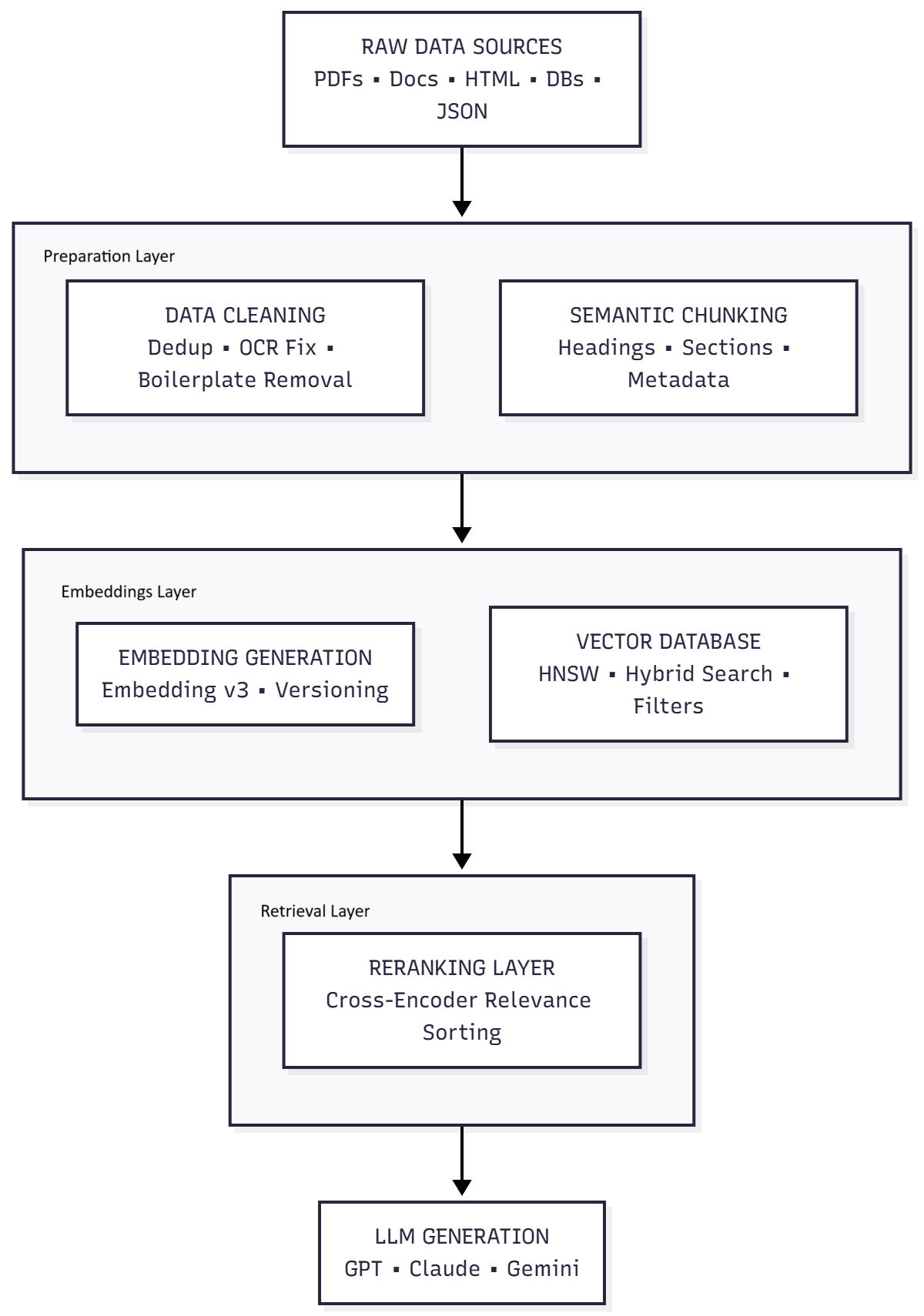
How to fix it?
Step 1: Map Your Data Landscape
Before optimizing anything, understand what you’re working with.
Inventory your datasets:
- Where does the data live? (filesystems, cloud buckets, SharePoint)
- What formats? (PDF, DOCX, HTML, emails, JSON, DB rows)
- How frequently does it change?
- How many total documents?
Create a simple table:
Dataset | Format | Size | Updated? | Issues |
Knowledge base | 4GB | Monthly | Long pages, no metadata | |
FAQs | Markdown | Small | Rarely | Good |
CRM notes | JSON | Large | Daily | No timestamp sorting |
Contracts | Scanned PDFs | Large | Rarely | OCR quality weak |
This tells you where quality is leaking before you embed anything.
Step 2: Clean and Normalize Before Embedding
Embedding garbage → retrieving garbage.
Key preprocessing steps:
- Deduplicate documents
Duplicate content confuses vector search engines like Pinecone Vector Database
https://www.pinecone.io
and open-source systems like Milvus Vector Database
https://milvus.io
- Convert PDFs properly
Avoid naive PDF-to-text extraction.
Use structured extraction (e.g., PyMuPDF or PDFMiner).
- Fix OCR errors
Especially for scanned docs.
Bad OCR = irrelevant chunks.
- Remove boilerplate
Headers, footers, page numbers, disclaimers add noise.
- Split documents semantically
Not by random token count.
Use:
- Headings
- Paragraphs
- Table boundaries
- Section-level context
- Hierarchical chunking (parent-child relationships)
The rule:
Your chunk should contain enough meaning to stand alone.
Step 3: Use Smart Chunking (Your Biggest Lever)
Chunking determines your entire retrieval quality.
Bad chunking → noisy retrieval
Good chunking → precise, relevant RAG
Tools like LangChain’s RAG Guide outline best practices for chunking and retrieval pipelines:
https://python.langchain.com/docs/use_cases/question_answering/
Use hierarchical metadata such as:
title
section
subsection
page
Recommended chunk size: 150–400 tokens
Add metadata like:
source_file
topic
author
timestamp
embedding_version
This step alone improves retrieval more than any hardware upgrade.
Step 4: Add Metadata (Don’t Rely on Embeddings Alone)
Retrieval = vector similarity + metadata filters + keyword search
Metadata is crucial when using vector databases such as:
Weaviate (Hybrid search with BM25 + vectors)
https://weaviate.io/developers/weaviateFAISS (Facebook AI Similarity Search) (high-performance indexing)
https://faiss.ai
Good metadata allows your queries to be FAST and ACCURATE.
Examples of useful metadata fields:
- Date / version
- Category
- Section title
- Document type
- Tags
- Confidence scores (OCR, parsing)
Example filter:
Filter:
{
"document_type": "policy",
"effective_year": { "$gte": 2023 }
}
Filtering removes 80% irrelevant chunks before vector search begins.
Step 5: Tune Your Vector Store (Most Teams Skip This)
Your vector DB is NOT configured optimally out of the box.
Key parameters to tune:
Parameter | Why It Matters |
Top-k | Too high → noisy results; Too low → missing context |
Distance metric | cosine vs dot product affects similarity ranking |
Index type | HNSW, IVF-PQ, disk-based vs memory-based |
Merging strategy | Many small indexes slow retrieval |
Filters before vectors | Faster + more accurate |
Practical recommendations:
- Start with top_k = 3–5
- Use cosine similarity for general text
- Enable hybrid search (keyword + embeddings)
- Use HNSW index for fast recall
- Periodically rebuild indexes to avoid fragmentation
Step 6: Use Reranking to Fix Retrieval Quality
Even with good embeddings, top_k may include mediocre chunks.
Add a reranking model (e.g., BAAI/bge-reranker or Cohere Rerank) to reorder results based on semantic closeness.
Why reranking matters:
- Embeddings → find roughly relevant items
- Reranker → precisely orders them
Massive quality boost for:
- Legal
- Medical
- Financial documents
- Long-form knowledge bases
Step 7: Cache Aggressively (Reduce Cost + Latency)
Two caching layers matter:
- Query caching
Store LLM answers for repeated questions.
(Especially in support bots, analytics Q&A, documentation assistants.)
- Retrieval caching
Cache vector-store results for common queries.
- Chunk caching
Don’t re-embed unchanged documents.
Store hash → embedding map.
Step 8: Enforce Embedding Versioning
Never mix embeddings created with different models.
Add metadata:
"embedding_version": "text-embedding-3-large" This prevents:
- Ranking inconsistencies
- Retrieval mismatch
- Silent accuracy drops
Step 9: Evaluate Retrieval (Not Just LLM Output)
A good RAG system measures:
- Precision@k
- Recall@k
- Coverage
- Latency per retrieval step
- Token cost reduction
When retrieval is correct, the LLM output becomes consistent and cheap.
Final Result: A Faster, Cheaper, More Reliable AI System
After applying these steps, your pipeline will:
- Retrieve faster
- Deliver more accurate answers
- Reduce hallucinations
- Lower token usage by 40–80%
- Improve user experience
- Scale properly
The model was never the problem.
Your data layer was.
Fix the pipeline → your AI suddenly feels 10× smarter.
As the Tech Co-Founder at Yugensys, I’m driven by a deep belief that technology is most powerful when it creates real, measurable impact.
At Yugensys, I lead our efforts in engineering intelligence into every layer of software development — from concept to code, and from data to decision.
With a focus on AI-driven innovation, product engineering, and digital transformation, my work revolves around helping global enterprises and startups accelerate growth through technology that truly performs.
Over the years, I’ve had the privilege of building and scaling teams that don’t just develop products — they craft solutions with purpose, precision, and performance.Our mission is simple yet bold: to turn ideas into intelligent systems that shape the future.
If you’re looking to extend your engineering capabilities or explore how AI and modern software architecture can amplify your business outcomes, let’s connect.At Yugensys, we build technology that doesn’t just adapt to change — it drives it.
Subscrible For Weekly Industry Updates and Yugensys Expert written Blogs